MOEBIUS - Moebius
| English | Vietnamese |
The game of Moebius is not well known, but there are some fanatics who spend their whole day playing it. In this game, the player is to find the way to clear a pair of squares containing x and z on a Moebius with the minimum cost.
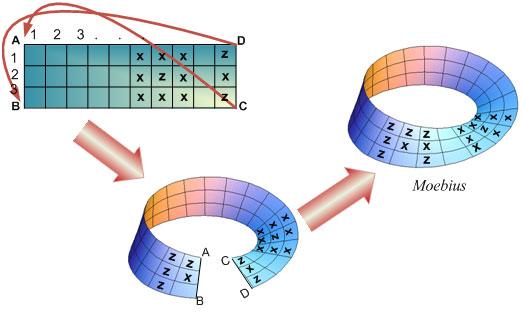
A Moebius is made from a rectangular M×N paper, namely ABCD. Each face of this paper consists of a rectangular grid of equivalent squares 1×1 . On both grids, columns are sequentially numbered from 1 to N and rows are sequentially numbered from 1 to M, all starting at A corner. In addition, every square (i, j), located at row i and column j, can contain x, z or nothing (empty square). Taking this paper and giving it a half-twist, then joining the ends together, A with C and B with D, to form a single band, we have a Moebius, which has only one surface, for this game.
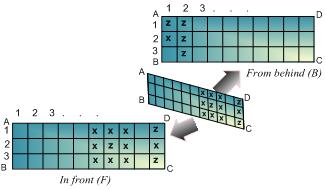
|
|
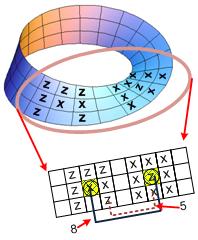
One clearance of a pair of squares containing x and z could be executed only if there is a direct path between two squares through consecutive 4 neighboring empty squares with at most two left or right turns. The intermediate empty squares may locate out of the Moebius. The cost to clear a pair of squares containing x and z is the length of the shortest direct path between two squares. After a clearance, the two original squares containing x and z become empty. The figure above shows two consecutive clearances with the cost of 5 and 8 respectively.
Your task is to write a program to perform one clearance to remove a given pair of squares containing x and z, with the minimum total cost using at most one extra intermediate clearance.
Input
The input file consists of several data sets. The first line of the input file contains the number of data sets which is a positive integer and is not bigger than 20. The following lines describe the data sets.
For each data test, the first line contains 2 integers M and N (1 ≤ M, N ≤ 1000) separated by space. The next two lines contain 3-tuples of the form 'C u v' describing the two squares to remove, where C is either 'F' for the front surface or 'B' for the back surface, u (1 ≤ u ≤ M) and v (1 ≤ v ≤ N) are integer coordinates on the original rectangular surface.
The next M lines describing the front surface of the Moebius. The i-th line in these M lines contains N consecutive characters where each character can be x, z or "." ("." for empty), describing the i-th row of the front surface.
The next M lines describing the back surface of the Moebius. The j-th line contains N consecutive characters where each character can be x, z or "." ("." for empty), describing the j-th row of the back surface.
Output
For each data test, write in one line the minimum total cost. Write '-1' if the given pair cannot be cleared using at most one intermediate clearance.
Example
Sample Input 1 3 10 F 2 7 B 2 1 .....xxx.z .....xzx.x .....xxx.z .z........ xz........ zz........ Sample Output 13
hide comments
|
|
Oleg:
2025-06-26 08:19:59
From description it was not clear if we can go outside from "front" and then return back to "back" side of Moebius....
|
| Added by: | Jimmy |
| Date: | 2009-01-04 |
| Time limit: | 30s |
| Source limit: | 50000B |
| Memory limit: | 1536MB |
| Cluster: | Cube (Intel G860) |
| Languages: | All except: ERL JS-RHINO NODEJS PERL6 VB.NET |
| Resource: | ACM Regional, Ho Chi Minh City 2008 |

 RSS
RSS