| Submit | All submissions | Best solutions | Back to list |
ABCPATH - ABC Path |
You will be given a 2-dimensional grid of letters. Find the length of the longest path of consecutive letters, starting at 'A'. Paths can step from one letter in the grid to any adjacent letter (horizontally, vertically, or diagonally).
For example, in the following grid, there are several paths from 'A' to 'D', but none from 'A' to 'E':
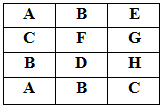
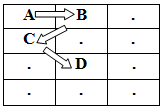
One such path is:
Input
Each test case will start with a line contains two integers H, W the height and width of the grid respectively 1 <= H, W <= 50. Then H lines follow each of W uppercase letters only. Input terminates with H = 0 and W = 0.
Output
For each test case print “Case C: X” without quotes where C is the case number starting with 1 and X is the solution.
Example
Sample Input: 4 3 ABE CFG BDH ABC 0 0 Sample Output: Case 1: 4
| Added by: | Ali Arous |
| Date: | 2011-11-05 |
| Time limit: | 1s |
| Source limit: | 50000B |
| Memory limit: | 1536MB |
| Cluster: | Cube (Intel G860) |
| Languages: | All except: ASM64 |
| Resource: | FCIS Local Contest 2012 |
hide comments
|
||||||||||||||
|
2019-09-02 08:41:58
Don't forget that the sequence must start from 'A'. Hint: Simply use recursion+memoization. |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-08-26 20:22:51
my code gives runtime error anyone suggests me why they give run time error. |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-08-12 08:20:54
mohaimin66: thank u so much bro : ) |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-08-01 21:45:32
Seems like easy dfs to me at first but accepted after 3rte and 4wa Last edit: 2019-08-01 23:40:58 |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-07-16 19:09:58
Don't forget to write Case costed me 2WA |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-06-29 18:25:07
@shiv pratap singh can you explain the approach this is what i tried and i am getting wrong ans https://ideone.com/h5yPE3 |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-06-29 18:17:05
will anyone explain me why this is giving wrong ans https://ideone.com/h5yPE3 |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-06-18 15:47:30
Good problem to practice on dfs on 2D and a bit of dp required.... |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-05-28 07:58:45
me_milan thank you so much without memorize got two time TLE >> simple dfs+direction array+dp(memrization) happy coding |
||||||||||||||
|
2019-05-20 19:06:51
dont go back to A after Z caused me 2 WAs . :( |
||||||||||||||


 RSS
RSS